The medial femoral condyle is located on the inside part of the knee whereas the lateral femoral condyle which is bigger is. Contents Clinical significance Additional images References External links Clinical significance.

Medial Condyle Of Femur Wikipedia
There is a significant difference in articular cartilage thickness between the medial and lateral posterior femoral condyles in patients undergoing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.

. O Gluteus maximus and tensor both insert on lateral condyle of tibia via the iliotibial tract Iliotibial tract o Lateral thickening of the fascia sleeve Gluteal tuberosity o Lateral swing of linea aspera o Insertion of gluteus maximus Trendelenburg Gait Drop of hip due to weak hip abductors medius and minimus Common Attachments 6 Insertions. 4 rows In other words the lateral surface of the medial condyle the medial wall of the. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
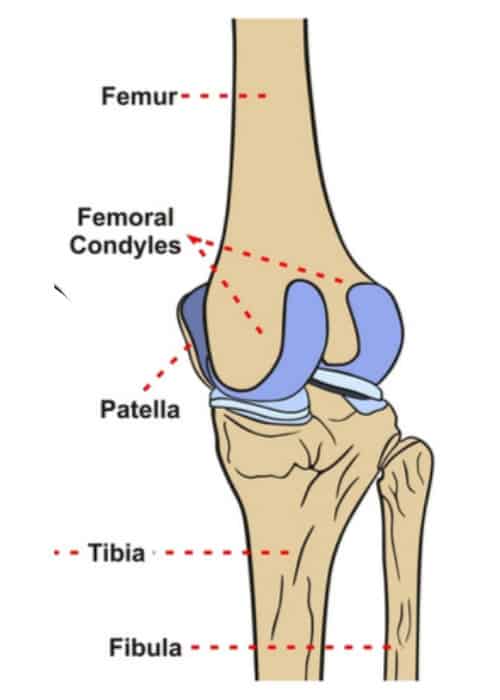
There are two femoral condyles. The femoral condyles are the two rounded prominences at the end of the femur. Interface of the medial and lateral femoral condyles.
The articular cartilage thickness on the medial posterior femoral condyle was 3 mm 1 mm mean standard deviation and 1 mm 1 mm on the lateral side p-value. They are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa proximally bounded by the horizontal intercondylar line. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. These results showed that a gender-specific or asymmetric femoral component design is required to regenerate the coronal. The posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee while the anterior surface articulates with the patella.
They are the pair of rounded eminences that form the. Intercondylar fossa A depression found on the posterior surface of the femur it lies in between the two condyles. They are called the medial and the lateral femoral condyle respectively.
While both bones feature a medial and lateral condyle with the lateral condyle on the other side of the knee the medial condyle is the larger prominence because more weight is transferred across the inside aspect of the knee joint. There are two condyles on each leg known as the medial and lateral femoral condyles. They are the area of attachment of some muscles and the collateral ligaments of the knee joint.
The study provided a reliable and consistent evaluation of the coronal curvature of femoral condyles in the Korean population. In the 155 varus knees the radius of the lateral condyle was an average of 01 mm larger than that of the medial condyle p 0003. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
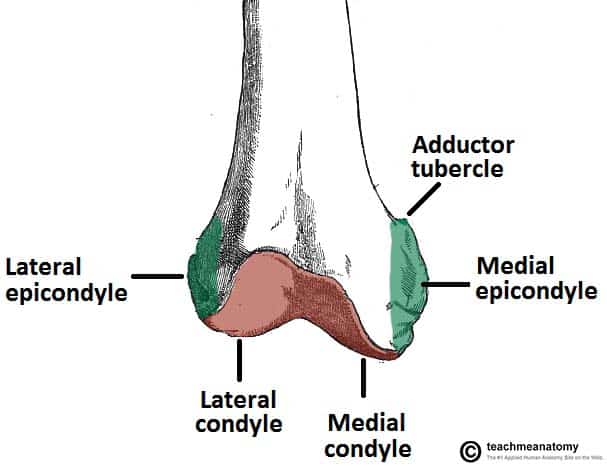
The other one is the medial condyle. Simply so where are the medial and lateral condyles. At the end of the medial supracondylar line is a tubercle called the adductor tubercle.
Cartilage thickness of the lateral posterior femoral condyle and medial posterior femoral condyle was recorded and expressed in millimeters mm. Medial and lateral condyles rounded areas at the end of the femur. If there is a fracture break in part of the condyle this is known as a fracture of the femoral condyle.
The motions of the condyles include rocking gliding and rotating. Learn more about the femur in this. Furthermore the medial and lateral coronal curvatures of the femoral condyle were symmetric in all TKA implant designs.
On each condyle is a smaller epicondyle which serve as the point of attachment for the collateral ligaments the medial collateral MCL and the lateral collateral ligaments LCL. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. D 0336 WDC -0097 WMC -0153 DLC 0372 DIN - 20912.
Medial and lateral epicondyles Bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles. Physiotherapy is very important during the rehabilitation following a femoral condyle fracture. In between the medial and lateral femoral condyles is the intercondylar fossa.
The paired femoral condyles are situated to either side of the patella or kneecap. Projecting from each condyle is an epicondyle that act as attachment sites for the collateral ligaments. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle.
The lateral condyleis one of the two projections on the lower extremity of the femur. The p-value for statistical significance was set at 005. The most accurate equation used width of the medial and lateral condyles WDC with of the medial condyle WMC depth of the lateral condyle DLC and depth of the intercondylar notch DIN 941 and is as follows.
Similar to the articular surface of the patella the trochlear surface is divided into medial and lateral facets the lateral facet being larger and extending more proximally and anteriorly than its medial counterpart Figure 22-2. Blood Supply edit edit source The femoral artery is the main blood. Prominent lateral and medial condyles are found at the distal end of the femur.
The medial and lateral condyles form the proximal part of the body of femur and articulate with the proximal part of tibia to form the femorotibial joint. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is broader both in its front-to-back and transverse diameters. The lateral condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of the femur.
Any abnormal surface structure or cartilage damage can lead to cartilage breakdown and arthritis loss of cartilage padding. The lateral and medial condyles are separated by the intercondylar notch. The medial and lateral condyles of the tibia articulate with the The head of the femur articulates with the hip bone at the The ligament that helps to maintain the alignment of the condyles between the femur and tibia and to limit the anterior movement of the tibia on the femur is the.
A femoral condyle is the ball-shape located at the end of the femur thigh bone. Differences in articular cartilage thickness between the means of these two groups medial and lateral were evaluated using Students t-test. Anatomical terms of bone.
The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is broader both in its front-to-back and transverse diameters. Left knee-joint from behind showing interior ligaments.
The femoral condyles form the trochlear groove that provides the articulating surface of the femur. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. The radius of a condyle was the average of the radii on four adjacent images that showed the femoral condyle with the largest curvature.
The other one is the medial condyle.

Femur An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The Femur Proximal Distal Shaft Teachmeanatomy
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture
Femoral Condyle Articular Cartilage Injury Minneapolis St Paul Edina Eagan Mn


0 comments
Post a Comment